Cytotoxicity tests on medical devices
Cytotoxicity tests are essential for assessing the cleanliness and biocompatibility of medical devices. These tests specifically measure the toxic effect that a material can have on cell structures and are part of the DIN EN ISO 10993-5 standard. The aim is to ensure that the products have no harmful effect on cells and are therefore safe to use. The extraction and incubation times, which can vary depending on the product, are essential for a reliable assessment of the cytotoxicity of medical devices. The reproducibility of the tests, particularly in the case of repeat tests or tests as part of monitoring, is also of crucial importance.
Test procedure
The testing procedure for cytotoxicity tests involves several steps to ensure that the products tested do not have any harmful effects on cells:
- Sample preparation: medical devices are extracted in a suitable medium for 4 to 72 hours to dissolve potentially toxic substances.
- Cell culture: Suitable cell lines such as fibroblasts or epithelial cells are used as they have a high sensitivity to toxic substances.
- Incubation: The cells are incubated with the extract of the product for a defined period of time (24 to 72 hours).
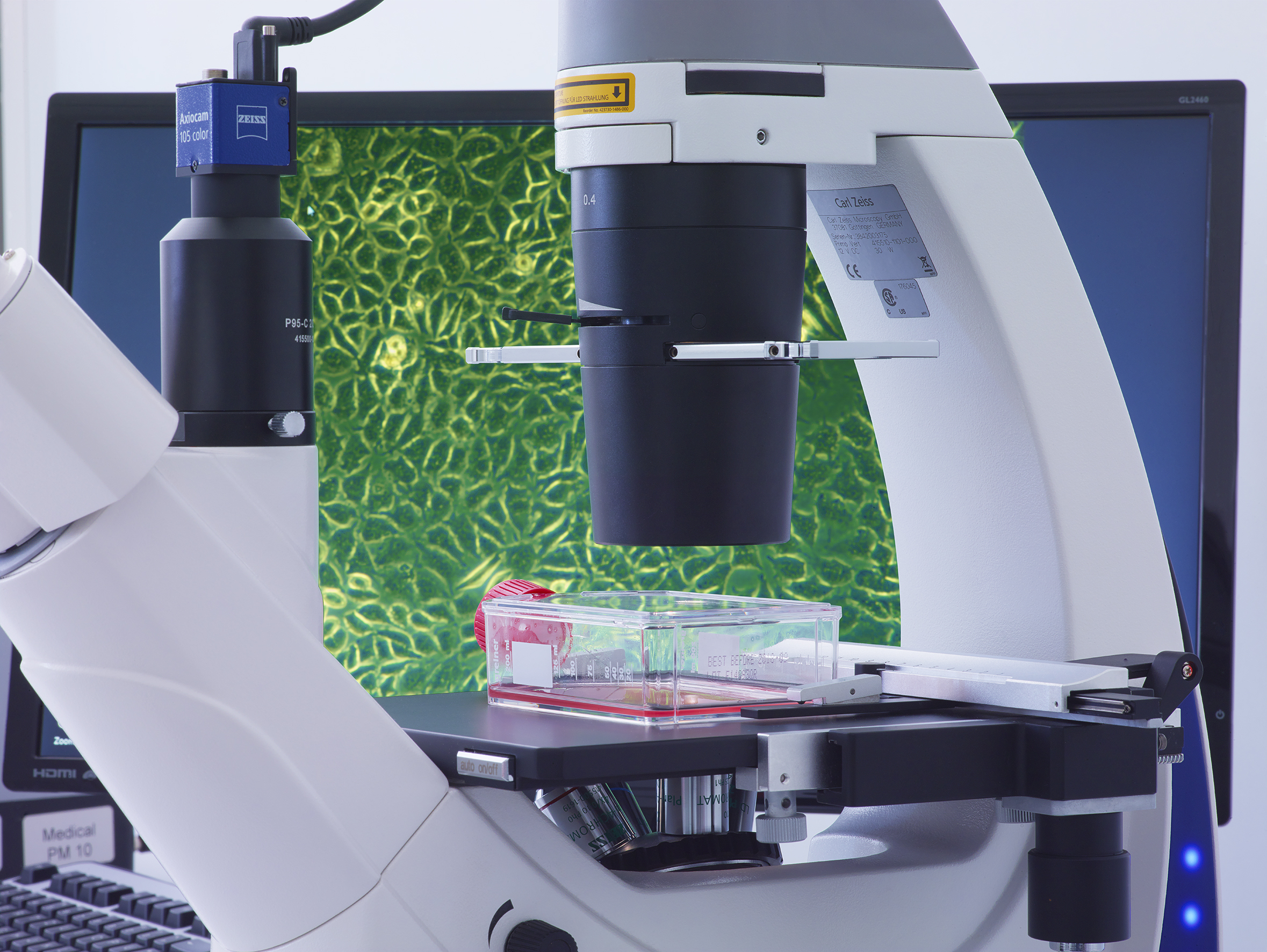
- Observation: After incubation, the cells are examined under the microscope for morphological changes and growth behavior.
- Evaluation: A quantitative result is determined. This can be done using various methods, depending on the question and regulatory requirements.
Cell lines
Cell lines are cultured cells that are widely used in research and in tests such as cytotoxicity assays. They provide a consistent and reproducible platform for evaluating cell responses to various substances. Commonly used cell lines include:
- Fibroblasts: These cells are particularly sensitive to toxic substances and are commonly used in cytotoxicity assays and are also used in clean controlling.
- Epithelial cells: These cells are also widely used and are well suited for tests that evaluate the interaction of materials with cell surfaces.
Specific requirements for cell lines
- Authenticity: The cell lines must be verified and free of contamination.
- Passage number: Cells should be in a low passage number to avoid genetic drift.
- Culture conditions: Culture conditions must be standardized, including temperature, CO₂ concentration and culture medium.
Extraction and incubation times
Extraction and incubation times are decisive parameters in cytotoxicity tests. They vary depending on the type of medical device. The following options can be used as an initial guideline, but the final decision must be made by the manufacturer based on a risk assessment:
Extraction time:
- Non-critical devices: 24 hours (4 hours also possible for short-term use with justification from the manufacturer)
- Implants: 72 hours
Incubation time:
- Non-critical products: 24 hours
- Standard instruments: 48 hours
- Implants: 72 hours
Evaluation methods
There are various evaluation methods for cytotoxicity tests, which are described in the standard DIN EN ISO 10993-5. These methods are suggestions and are not binding. The common methods include
- MTT test: measures cell viability by the reduction of MTT to formazan.
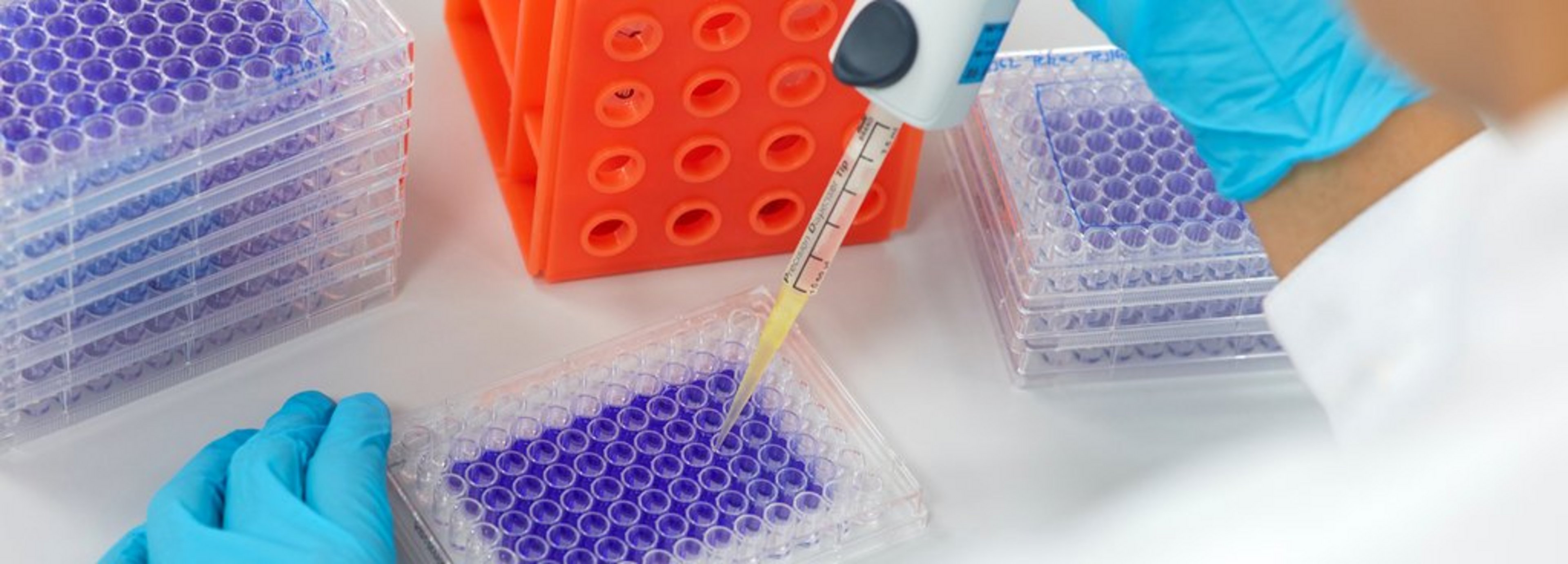
- Crystal violet staining: This method is used to quantitatively assess cell viability.
Comparison of the evaluation methods
MTT test:
- Advantages: High sensitivity, widely used, quantitative.
- Disadvantages: Can be affected by certain substances that interfere with the reduction of MTT.
Crystal violet staining:
- Advantages: Easy to perform, quantitative, reliable.
- Disadvantages: Can be influenced by cell overlay, requires careful performance.
Crystal violet staining
CleanControlling's preferred method of analysis is crystal violet staining, which has been used as standard at CleanControlling for years and is also accredited. This method is also recognized by the FDA.
Crystal violet staining procedure
- Fixation: After incubation, the cells are fixed in order to preserve their structure.
- Staining: the fixed cells are stained with crystal violet, a dye that binds to the cells' DNA.
- Washing: Excess dye is washed off to retain only the stained cells.
- Evaluation: The bound dye is returned to solution, resulting in a colored liquid whose intensity correlates with the number of cells present.
Recommendation
To ensure comparability with previous analyses, we recommend that the extraction and incubation times are generally retained. These are listed in the final reports. However, new parameters are also possible. These parameters, which are important for the test, can be specified by the client in the TEST ITEM CHARACTERIZATION SHEET and thus form the basis for the subsequent test planning.
General recommendation
For implants:
- Extraction time: 72 hours
- Incubation time: 72 hours
For products other than implants:
- Extraction time: 24 hours
- Incubation time: 48 hours
Conclusion
The use of proven evaluation methods is essential for a reliable assessment of the cytotoxicity of medical devices. The extraction and incubation times, which can vary depending on the product, are essential for a reliable evaluation of the cytotoxicity of medical devices. Consistent extraction and incubation times are crucial for the reproducibility of tests, especially in the case of repeat tests or tests as part of monitoring. These measures help to ensure the safety and biocompatibility of the products.
Newsletter registration